Hydraulic Press vs. Electric Press: A Comprehensive Comparison

This passage can serve as a foundation for creating a comprehensive comparison between hydraulic and electric presses, helping readers understand the differences and make informed decisions based on their specific needs and applications.

Operating Principles
hydraulic press
A hydraulic press operates on the fundamental principle of Pascal’s Law, which states that when pressure is applied to a confined fluid, it is transmitted undiminished in all directions. The key components of a hydraulic press include a hydraulic cylinder, a piston, and a hydraulic fluid reservoir.
The hydraulic press begins by filling the hydraulic cylinder with a hydraulic fluid (typically oil). A mechanical force is applied to the piston, which compresses the hydraulic fluid in the cylinder. Pascal’s Law comes into play here, and the pressure is distributed evenly throughout the fluid.
The press’s hydraulic system is designed to amplify force. A small force applied to the piston results in a larger force exerted on the workpiece. This amplified force is used to perform various tasks, such as bending, punching, or forming materials.

Hydraulic presses are powerful and versatile machines that find extensive use in various industries due to their unique advantages. However, like any technology, they also come with certain operational limitations. In this article, we will explore the strengths and constraints of hydraulic presses.
Advantages of Hydraulic Press
High Force Capability:
Hydraulic presses can generate immense force, making them suitable for tasks that require substantial pressing, bending, or molding. This high-force capability is particularly advantageous in industries like metalworking and manufacturing.
Precision Control:
Hydraulic presses offer precise control over force and speed. Operators can adjust parameters to ensure accurate and repeatable results, which is crucial in applications demanding tight tolerances.
Versatility:
Hydraulic presses are adaptable and can accommodate a wide range of tooling and dies. This versatility allows them to perform various tasks such as stamping, deep drawing, and extrusion, making them indispensable in industries like automotive and aerospace.
Quiet Operation:
Compared to mechanical presses, hydraulic presses operate more quietly. The fluid-based system absorbs noise and vibrations, creating a quieter working environment, which is beneficial in settings where noise reduction is a concern.
Safety Features:
Hydraulic presses are equipped with safety features like emergency stop buttons and pressure relief valves. These mechanisms ensure operator safety by quickly stopping or releasing pressure in case of an emergency.

Operational Limitations of Hydraulic Press:
Complex Maintenance:
Hydraulic presses require regular maintenance of hydraulic fluid and seals. Maintaining the hydraulic system can be complex and time-consuming, leading to downtime if not performed correctly.
Energy Consumption:
Hydraulic presses tend to be less energy-efficient compared to electric presses. They continuously consume energy to maintain hydraulic pressure, which can result in higher operating costs over time.
Fluid Leakage:
Hydraulic systems can experience fluid leakage if seals or hoses deteriorate. This not only leads to environmental concerns but also reduces the efficiency and reliability of the press.
Slower Cycling Times:
While hydraulic presses offer precision and high force, they may have slower cycling times compared to electric or pneumatic alternatives. This limitation can affect productivity in applications requiring rapid operation.
Heat Generation:
The continuous compression and release of hydraulic fluid generate heat. In some cases, this heat buildup can affect the accuracy and longevity of the press’s components.
Electric Press

An electric press, on the other hand, employs an entirely different working principle based on electric motors and mechanical components.
The electric press is equipped with an electric motor, which converts electrical energy into mechanical motion.
When the motor is energized, it generates rotational motion, which is then transferred to the press’s working components.
In an electric press, this mechanical motion is transferred to various components like a ram, a slide, or a platen.
These components apply force to the workpiece, allowing for processes like stamping, blanking, or shearing.
An electric press, also known as an electrically driven press, is a versatile industrial machine used for various manufacturing and material processing applications. It relies on electrical power to generate force and motion.
Advantages of Electric Press Machines:
Precision Control:
Advantage: Electric press machines offer precise control over force, speed, and position. Operators can program and adjust these parameters to achieve highly accurate and repeatable results, making them ideal for applications requiring tight tolerances.
Energy Efficiency:
Advantage: Electric presses are known for their energy efficiency. They consume power only when in operation, reducing energy costs and environmental impact compared to hydraulic systems that maintain pressure even when idle.
Quiet Operation:
Advantage: It operates quietly, creating a more comfortable and noise-sensitive work environment. This feature is beneficial in industries where noise reduction is a concern, such as electronics manufacturing or cleanrooms.
Low Maintenance:
Advantage: They generally require less maintenance compared to hydraulic presses. They do not have hydraulic fluids or seals that need frequent servicing, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
Speed and Responsiveness:
Advantage: Electric press machines have rapid response times, allowing for high-speed operation and quick tool changes. This makes them suitable for applications demanding fast cycle times, such as high-volume production.

Operational Limitations of Electric Press Machines
Limited Force Range:
Limitation: Electric presses may have limitations in terms of the maximum force they can generate compared to hydraulic presses. This can restrict their suitability for heavy-duty applications requiring extreme force.
Initial Cost:
Limitation: Electric press machines typically have a higher initial purchase cost compared to hydraulic counterparts. However, this cost difference may be offset by long-term energy savings and lower maintenance expenses.
Overload Risks:
Limitation: Electric presses are sensitive to overloads, which can damage the machine or cause tooling failure. Proper load monitoring and safety systems are essential to prevent such incidents.
Heat Generation:
Limitation: Continuous operation of electric presses can generate heat, potentially affecting the accuracy and longevity of machine components. Cooling systems may be necessary for extended use.
Limited Application Range:
Limitation: Electric press machines are highly suitable for specific applications but may not be the best choice for all tasks. Their suitability depends on factors such as force requirements, cycle times, and the nature of the materials being processed.
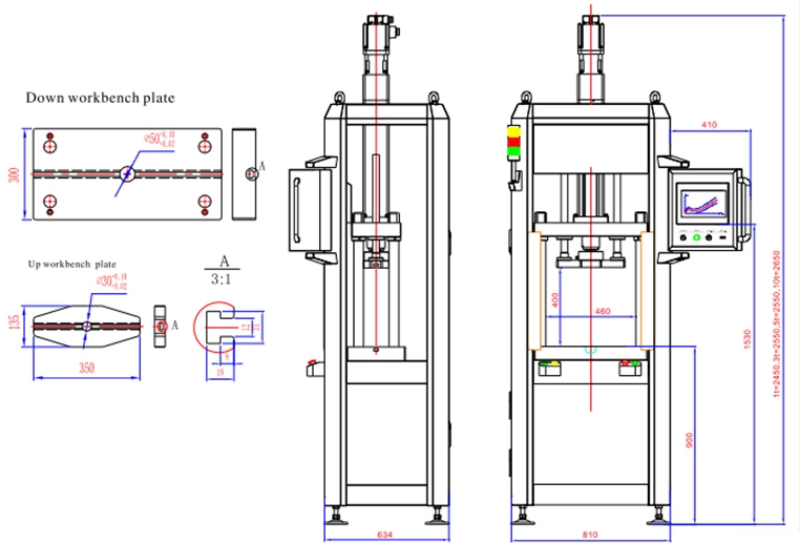
Performance and Efficiency
Performance Comparison:
Force Generation:
Hydraulic presses are known for their exceptional force generation capabilities. They can exert high levels of force, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications such as metal forming and forging.
Electric presses, while powerful, may have limitations in terms of maximum force output. They are often favored for tasks requiring moderate to high force with precision.
Speed and Precision:
Hydraulic presses offer precise control over speed and force but are generally slower in operation compared to electric presses.
Electric presses excel in rapid response times and precise control, making them suitable for applications demanding high-speed and accurate performance.
Versatility:
Hydraulic presses are versatile and can accommodate a wide range of tooling and dies, making them suitable for various tasks like stamping, bending, and extrusion.
Electric presses are also versatile and adaptable, offering a broad range of applications, especially those requiring precise force and position control.
Efficiency Comparison:
Energy Efficiency:
Hydraulic presses are typically less energy-efficient than electric presses. They continuously consume energy to maintain hydraulic pressure, even when not in active use.
Electric Presses are more energy-efficient as they only consume power during operation, leading to reduced energy costs and a smaller environmental footprint.
Maintenance Requirements:
Hydraulic Press require regular maintenance of hydraulic fluid and seals, which can be time-consuming and costly. Leaks and fluid changes are common maintenance tasks.
Electric presses generally have lower maintenance requirements since they do not rely on hydraulic fluids or seals. This reduces downtime and maintenance costs.
Noise Level:
Hydraulic Press can produce considerable noise due to hydraulic fluid flow and the operation of hydraulic components.
Electric Press operates quietly, creating a more comfortable and noise-sensitive working environment.
Environmental Impact:
Hydraulic Press can pose environmental concerns due to the use and disposal of hydraulic fluids. Fluid leaks can also be problematic.
Electric Press have a smaller environmental impact due to reduced energy consumption and the absence of hydraulic fluids.

Maintenance and Durability
Maintenance Comparison
Hydraulic Presses:
Maintenance Requirements: Hydraulic presses often require more maintenance due to their hydraulic fluid systems. Regular checks, fluid changes, and seal replacements are essential to prevent leaks and ensure proper operation.
Complexity: The hydraulic components in these presses, such as pumps, valves, and hoses, require careful maintenance to avoid breakdowns and downtime.
Cost: Maintenance costs for hydraulic presses can be relatively high due to the need for hydraulic fluid, seals, and skilled technicians.
Electric Presses:
Maintenance Requirements: Electric presses generally have lower maintenance requirements. They do not rely on hydraulic fluids or seals, reducing the risk of leaks and the associated maintenance tasks.
Simplicity: The absence of hydraulic components simplifies maintenance. Routine checks of electrical connections, motor lubrication, and control systems are typically sufficient.
Cost: Electric presses tend to have lower long-term maintenance costs compared to hydraulic presses.

Durability Comparison
Hydraulic Presses:
Durability: Hydraulic presses are known for their robustness and durability, particularly in heavy-duty applications. They can withstand high loads and harsh working conditions, making them suitable for demanding tasks.
Longevity: With proper maintenance, hydraulic presses can have a long service life, even in challenging industrial environments.
Resilience: Hydraulic systems can tolerate occasional overloads, which can help prevent damage to the press.
Electric Presses:
Durability: Electric presses are durable and can offer a long service life, especially when used within their designed load capacities and cycle rates.
Precision Components: Some electric press models use precision components that require careful operation and may be less forgiving of overloads or misuse.
Application-Dependent: The durability of electric presses depends on the specific application and the level of force and speed required. They may not be as suitable for extremely heavy-duty tasks as hydraulic presses.
In summary, hydraulic presses are renowned for their durability in heavy-duty applications but require more complex maintenance due to hydraulic systems and fluids. On the other hand, electric presses offer lower maintenance requirements and can be durable when used within their specified parameters. The choice between the two depends on the specific manufacturing needs, considering factors like force, speed, maintenance budgets, and the working environment. Both types of presses can provide reliable performance when properly maintained, ensuring longevity and productivity in industrial settings.