Safety Measures and Compliance Standards for Punching Machines

Punching machines are indispensable tools in modern manufacturing, facilitating the efficient processing of sheet metal and other materials. However, their powerful capabilities also pose significant safety risks if not operated and maintained properly. In this comprehensive guide, we explore essential safety measures and compliance standards that manufacturers and operators must adhere to when using punching machines.
Introduction to Punching Machines
Punching machines are mechanical or hydraulic devices designed to punch holes, shear, notch, and form sheet metal and other materials. They are widely used in industries such as automotive manufacturing, aerospace, construction, and electronics for their precision and versatility in sheet metal fabrication.
While advancements in technology have improved efficiency and accuracy, ensuring the safety of operators and maintaining compliance with industry regulations remains paramount. Let’s delve into the key aspects of safety and compliance for punching machines.

Understanding Safety Hazards
Punching machines involve various mechanical components and processes that can present hazards to operators and bystanders if not managed correctly. Some common safety hazards associated with punching machines include:
- Mechanical Hazards: Moving parts such as punches, dies, and feed mechanisms can cause crushing, shearing, or impact injuries if operators come into contact with them during operation.
- Electrical Hazards: Electrical systems powering the machine and its components pose risks of electric shock or fire if wiring is damaged or improperly installed.
- Ergonomic Hazards: Prolonged use of punching machines can lead to ergonomic issues such as repetitive strain injuries (RSIs) if ergonomic principles are not applied in machine design and operation.
- Noise and Vibration: High noise levels and vibrations generated during machine operation can affect operator health and safety if not adequately controlled.
Compliance Standards
To mitigate these risks, punching machines must comply with relevant safety standards and regulations established by governmental bodies and industry organizations. Here are some of the key standards applicable to punching machines:
1. OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) Standards:
In the United States, OSHA sets forth regulations that apply to the operation and maintenance of punching machines under its General Industry Standards (29 CFR Part 1910). Key requirements include:
- Ensuring machines are equipped with adequate guarding to prevent contact with moving parts.
- Conducting regular inspections and maintenance to keep machines in safe working condition.
- Providing training to operators on safe machine operation and emergency procedures.
2. European Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC):
In the European Union, the Machinery Directive mandates that punching machines and other machinery must meet essential health and safety requirements (EHSRs) to be placed on the market. Compliance involves:
- Conducting a risk assessment and implementing risk reduction measures (e.g., guards, safety devices).
- Ensuring machines bear the CE mark, indicating conformity with EU regulations.
- Providing instructions for use and maintenance in the appropriate language(s) of the intended user.
3. ISO Standards:
ISO standards provide internationally recognized guidelines for machinery safety and risk assessment. ISO 12100:2010, for example, outlines principles for risk assessment and risk reduction associated with machinery use, including punching machines.

Essential Safety Measures
To mitigate these risks and ensure a safe working environment, manufacturers and operators must implement the following essential safety measures:
1. Machine Guarding
Machine guarding is critical to preventing contact with hazardous areas of punching machines. Effective guarding solutions include:
- Fixed Guards: Install fixed barriers or enclosures around the point of operation, moving parts, and other hazardous areas to prevent access during machine operation.
- Interlocking Guards: Use guards equipped with interlocks that automatically stop the machine when the guard is opened or removed, preventing operation until the guard is securely closed.
- Light Curtains: Employ light-sensitive barriers that detect the presence of an operator’s hand or body within the danger zone, halting machine operation to prevent injuries.

2. Safety Training and Education
Proper training is essential for operators to understand safe operating procedures and emergency protocols when working with punching machines. Key aspects of training include:
- Machine Operation: Provide comprehensive training on how to safely operate punching machines, including startup, shutdown, and adjustment procedures.
- Hazard Identification: Educate operators on identifying potential hazards associated with punching machines and the importance of adhering to safety guidelines.
- Emergency Procedures: Train operators on emergency shutdown procedures and the use of emergency stop buttons to quickly halt machine operation in case of an accident or hazard.
3. Regular Maintenance and Inspections
Scheduled maintenance and routine inspections are vital to ensuring punching machines operate safely and efficiently. Maintenance practices should include:
- Scheduled Inspections: Conduct regular inspections of punching machines to check for worn parts, loose connections, and potential hazards that could compromise safety.
- Maintenance Checks: Follow manufacturer recommendations for lubrication, adjustment, and replacement of machine components to maintain optimal performance and safety.

4. Ergonomic Design Considerations
Designing workstations and machine controls with ergonomics in mind helps minimize operator fatigue and reduce the risk of musculoskeletal disorders. Ergonomic principles include:
- Workstation Layout: Arrange workstations to optimize operator comfort, posture, and reach, reducing strain during machine operation.
- Control Accessibility: Position machine controls and operating interfaces within easy reach and sight of operators to facilitate safe and efficient operation.
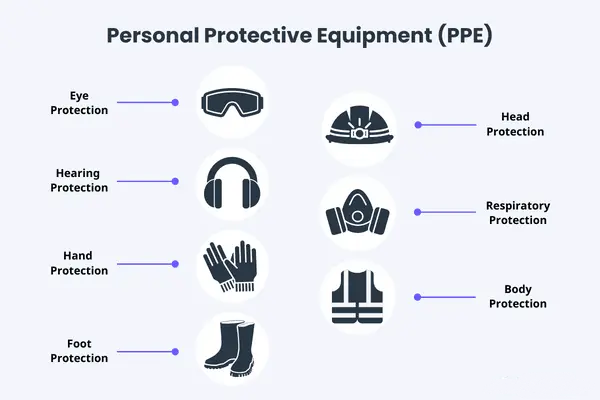
5. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Operators should wear appropriate PPE to protect against specific hazards associated with punching machines. Recommended PPE includes:
- Safety Glasses: Protect eyes from flying debris and metal shavings generated during punching and cutting operations.
- Hearing Protection: Reduce exposure to high noise levels produced by punching machines to prevent hearing damage over time.
- Gloves and Footwear: Wear gloves to protect hands from sharp edges and wear sturdy footwear with steel toes to prevent foot injuries.
Conclusion
Punching machines play a vital role in modern manufacturing, but their operation presents inherent safety risks that must be managed through adherence to stringent safety measures and compliance with regulatory standards. By prioritizing machine guarding, comprehensive training, regular maintenance, and ergonomic design principles, manufacturers can create safer working environments and mitigate the risk of accidents and injuries associated with punching machines.
Adherence to international standards such as OSHA regulations in the United States, the Machinery Directive in the European Union, and ISO guidelines ensures that punching machines are designed, operated, and maintained with the highest regard for safety and compliance. By integrating these practices into everyday operations, manufacturers can promote a culture of safety and enhance productivity in their facilities.







